Product Description
PRODUCT PARAMETER
| China Gearbox parts Drive Shaft ME636 | ||||||
|
Packing |
Carton Box with Brand / Nature Packing |
|||||
COMPANY INFORMATION
HangZhou CZPT Imp.& Exp.Co .,Ltd located in HangZhou,ZHangZhoug Province. Have been committed to developing & supplying Auto Transmission Parts,putting ourselves to clients’ shoes to solve their demands.our company is mainly engaged in Auto Transmission Parts such as Transmission gearbox,Gear haft,Synchronizer ring,Cylinder Head and Differcial Assembly and so on.
With our honesty and credit, we sincerely hope to cooperate with you for greater development. Welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and achieving mutual success!
WORLD-WIDE CUSTOMERS COMMENTS & FEEDBACK
Here is some of comments from our world-wide customers.
You can check all the comments at our company profile.
Please visit tashikomo
Click “company profile”,then choose “Rating & Reviews”
(please note: all our customer comments is real one………..)
We will package the product carefully and send it via EMS,DHL,or others…..
CONTACT
FAQ
★ What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent,
we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
★ What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages
before you pay the balance.
★Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Action now contact us for whole CATALOG.
MORE THEN 2000 KINDS OF OEM PARTS WAITTING FOR YHOU. PLEASE CONTACT US THE WHOLE CATALOG.
TRUST YOU WILL LIKE OUR DESIGNS & PRICE.
Please contat us for the WHOLE CATALOG. More than 2000 OEM PARTS.
WAITTING FOR YOU !!
ACTION NOW
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Type: | Shaft Gear |
| Material: | 20crmnti |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Automatic: | Manual |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2024-02-01
China OEM Drive Helical Gear Shaft with Alloy Steel for Gearbox
Product Description
Machining Capability
Our Gear, Pinion Shaft, Ring Gear Capabilities:
| Capabilities of Gears/ Splines | ||||||
| Item | Internal Gears and Internal Splines | External Gears and External Splines | ||||
| Milled | Shaped | Ground | Hobbed | Milled | Ground | |
| Max O.D. | 2500 mm | |||||
| Min I.D.(mm) | 30 | 320 | 20 | |||
| Max Face Width(mm) | 500 | 1480 | ||||
| Max DP | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | ||
| Max Module(mm) | 26 | 45 | 26 | 45 | ||
| DIN Class Level | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | DIN Class 8 | DIN Class 4 | ||
| Tooth Finish | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | Ra 3.2 | Ra 0.6 | ||
| Max Helix Angle | ±22.5° | ±45° | ||||
Our Main Product Range
1. Spur Gear
2. Planetary Gear
3. Metal Gears
4. Gear Wheel
5. Ring Gear
6. Gear Shaft
7. Helical Gear
8. Pinion Shaft
9. Spline Shaft
Company Profile
1. 21 years experience in high quality gear, gear shaft’s production, sales and R&D.
2. Our Gear, Gear Shaft are certificated by ISO9001: 2008 and ISO14001: 2004.
3. CZPT has more than 50 patents in high quality Gear, Gear Shaft manufacturing.
4. CZPT products are exported to America, Europe.
5. Experience in cooperate with many Fortune 500 Companies
Our Advantages
1) In-house capability: OEM service as per customers’ requests, with in-house tooling design & fabricating
2) Professional engineering capability: On product design, optimization and performance analysis
3) Manufacturing capability range: DIN 3960 class 8 to 4, ISO 1328 class 8 to 4, AGMA 2000 class 10-15, JIS 1702-1703 class 0 to 2, etc.
4) Packing: Tailor-made packaging method according to customer’s requirement
5) Just-in-time delivery capability
FAQ
1. Q: Can you make as per custom drawing?
A: Yes, we can do that.
2. Q: If I don’t have drawing, what can you do for me?
A: If you don’t have drawing, but have the sample part, you may send us. We will check if we can make it or not.
3. Q: How do you make sure the quality of your products?
A: We will do a series of inspections, such as:
A. Raw material inspection (includes chemical and physical mechanical characters inspection),
B. Machining process dimensional inspection (includes: 1st pc inspection, self inspection, final inspection),
C. Heat treatment result inspection,
D. Gear tooth inspection (to know the achieved gear quality level),
E. Magnetic particle inspection (to know if there’s any cracks in the gear).
We will provide you the reports 1 set for each batch/ shipment.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
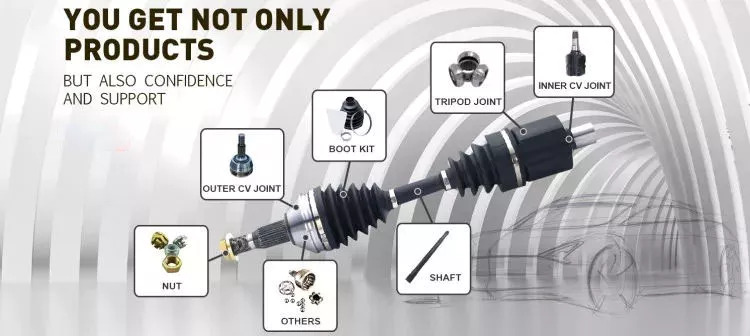
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2023-09-26
China manufacturer PYZ Series customized reverse gearbox helical gearbox with cyrcle pear ahaped gearbox vertical motor reductor transmission with Good quality
Warranty: 3 several years
Relevant Industries: Building Substance Retailers, Manufacturing Plant, Equipment Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Manufacturing facility, Farms, Property Use, Retail, Building works , Vitality & Mining, Advertising and marketing Business
Fat (KG): 65 KG
Tailored assistance: OEM, ODM, OBM
Gearing Arrangement: Cycloidal
Output Torque: 106-1571
Input Pace: 750-1500rpm
Certification: ISO9001-2008
Bearing: C&U
Packaging Information: Wooden Scenario or as asked for
PYZ Collection reverse gearbox for buggy helical gearbox with cyrcle pear ahaped gearbox vertical motor reductor transmission
Gain:PYZ collection hard tooth flank shaft-mounted reducer is designed by our company, the patent no.: ZL98116412.9. PYZ can be directly mounted on the driving enter shaft, no necessary to put in some plattorm, for connection among reducer and major device. Large in effectiveness, low in sounds. prolonged in provider daily life, compact in structure, TRC foot foundation and output flange variety aluminium helical reducer 1 1 ratio 90 degree equipment box aluminum 90 diploma gearbox gentle in weight, and straightforward to put in.
Firm Details
Top quality manage
Trade Displays
Packing&Shipping
Packing Particulars: Normal carton/Pallet/Standard wood scenario
Shipping and delivery Particulars : 15-thirty working times on payment
Related Product
Primary product record: 16 series like SLR/SLS/SLK/SLF series difficult tooth flank gear reducer , SLRC collection aluminium situation helical equipment reducers,SLHSLB collection higher energy velocity reducer, SLP collection planetary pace reducer, X/B series cycloidal reducer, SLXG sequence shaft-mounted equipment box, SLSWL collection worm screw jack, SLT sequence helical cone gear box, entirely far more than 10,000 ratios, different specification make us at the head of domestic transmission industry, broadly provide the mechanical transmission area of gentle & hefty business this sort of as: beer & beverage, mining equipment, Go Kart Forward Reverse Gearbox Fits Producer customized gearbox transmission meals packing, textile printing, rubber & plastic substance, petrochemical sector, jack-up transportation, pharmacy & procedure hides, environmental protection gear.
FAQ
one.Payment Expression: TT, L/C
two.Delivery time: about thirty days from get payment.
3.We acknowledge tailored products as per your special need.
4.Xihu (West Lake) Dis.lines for the Assortment:Generally we can decide on 1 device which is suitable for you with some informations from you,these kinds of as ratio/motor velocity/mounting dimension/ out torque and so on.
5.If the minimal order volume is in excessive of $ten thousand, there are preferential.
Q1: What information should I inform you to confirm the product?
A:Product/Size, Transmission Ratio, Shaft instructions & Purchase amount.
Q2: What can i do if I never know which 1 I need to have?
A:Dont worry, Ship as much info as you can, Higher High quality Block Sheave Pulley V Belt Pulley for Drilling Rig our staff will help you discover the right 1 you are searching for.
Q3: What is your product guarantee time period?
A:We supply 1 12 months guarantee since the vessel departure date left China.
If you have another query, pls really feel totally free to get in touch with us.
Get in touch with us
What is a push shaft?
If you notice a clicking noise whilst driving, it is most probably the driveshaft. An seasoned vehicle mechanic will be able to explain to you if the sound is coming from both sides or from 1 side. If it only transpires on 1 facet, you ought to verify it. If you recognize noise on equally sides, you should contact a mechanic. In possibly circumstance, a alternative driveshaft should be simple to uncover.
The generate shaft is a mechanical portion
A driveshaft is a mechanical system that transmits rotation and torque from the motor to the wheels of the car. This ingredient is vital to the operation of any driveline, as the mechanical electricity from the motor is transmitted to the PTO (electricity consider-off) shaft, which hydraulically transmits that power to linked equipment. Distinct push shafts contain distinct mixtures of joints to compensate for modifications in shaft length and angle. Some types of generate shafts incorporate connecting shafts, internal continuous velocity joints, and exterior fixed joints. They also incorporate anti-lock method rings and torsional dampers to stop overloading the axle or triggering the wheels to lock.
Even though driveshafts are relatively gentle, they need to have to deal with a good deal of torque. Torque used to the travel shaft creates torsional and shear stresses. Because they have to face up to torque, these shafts are made to be light-weight and have little inertia or bodyweight. Therefore, they typically have a joint, coupling or rod between the two components. Elements can also be bent to accommodate changes in the length among them.
The push shaft can be made from a assortment of resources. The most typical material for these parts is metal, despite the fact that alloy steels are frequently used for substantial-strength purposes. Alloy metal, chromium or vanadium are other components that can be used. The type of substance utilised is dependent on the application and size of the ingredient. In numerous instances, metallic driveshafts are the most resilient and least expensive option. Plastic shafts are utilized for light-weight duty programs and have different torque stages than metal shafts.
It transfers power from the motor to the wheels
A car’s powertrain is composed of an electrical motor, transmission, and differential. Each area performs a specific task. In a rear-wheel push vehicle, the electricity produced by the motor is transmitted to the rear tires. This arrangement improves braking and handling. The differential controls how much electricity every single wheel gets. The torque of the motor is transferred to the wheels according to its speed.
The transmission transfers electrical power from the motor to the wheels. It is also named “transgender”. Its work is to make certain electrical power is delivered to the wheels. Electric powered vehicles can’t drive them selves and demand a gearbox to travel forward. It also controls how considerably electrical power reaches the wheels at any given moment. The transmission is the last part of the electricity transmission chain. Even with its a lot of names, the transmission is the most complex ingredient of a car’s powertrain.
The driveshaft is a long metal tube that transmits mechanical energy from the transmission to the wheels. Cardan joints hook up to the push shaft and give adaptable pivot points. The differential assembly is mounted on the push shaft, enabling the wheels to change at different speeds. The differential makes it possible for the wheels to switch at various speeds and is extremely important when cornering. Axles are also crucial to the functionality of the car.
It has a rubber boot that safeguards it from dust and dampness
To keep this boot in great issue, you should clean it with chilly drinking water and a rag. In no way place it in the dryer or in direct daylight. Heat can deteriorate the rubber and cause it to shrink or crack. To prolong the existence of your rubber boots, apply rubber conditioner to them often. Indigenous peoples in the Amazon location acquire latex sap from the bark of rubber trees. Then they set their feet on the hearth to solidify the sap.
it has a U-formed connector
The generate shaft has a U-joint that transfers rotational strength from the engine to the axle. Faulty gimbal joints can result in vibrations when the car is in motion. This vibration is typically mistaken for a wheel equilibrium dilemma. Wheel equilibrium troubles can cause the motor vehicle to vibrate while driving, while a U-joint failure can result in the motor vehicle to vibrate when decelerating and accelerating, and end when the car is stopped.
The generate shaft is connected to the transmission and differential making use of a U-joint. It allows for small adjustments in position in between the two components. This prevents the differential and transmission from remaining properly aligned. The U-joint also enables the drive shaft to be linked unconstrained, permitting the automobile to go. Its primary purpose is to transmit electrical power. Of all varieties of elastic couplings, U-joints are the oldest.
Your vehicle’s U-joints must be inspected at minimum two times a year, and the joints ought to be greased. When examining the U-joint, you need to hear a boring audio when changing gears. A clicking seem suggests inadequate grease in the bearing. If you hear or feel vibrations when shifting gears, you may need to provider the bearings to prolong their life.
it has a slide-in tube
The telescopic design and style is a present day substitute to standard driveshaft types. This revolutionary layout is dependent on an unconventional layout philosophy that combines advancements in substance science and production procedures. For that reason, they are more successful and lighter than traditional patterns. Slide-in tubes are a simple and effective design remedy for any car application. Listed here are some of its benefits. Read on to discover why this sort of shaft is excellent for a lot of applications.
The telescopic travel shaft is an essential element of the conventional car transmission method. These driveshafts allow linear movement of the two components, transmitting torque and rotation during the vehicle’s driveline. They also take in energy if the motor vehicle collides. Often referred to as foldable driveshafts, their acceptance is immediately dependent on the evolution of the automotive industry.
It makes use of a bearing push to change worn or broken U-joints
A bearing press is a unit that makes use of a rotary press system to put in or remove worn or destroyed U-joints from a travel shaft. With this device, you can change worn or damaged U-joints in your automobile with relative ease. The very first step entails placing the travel shaft in the vise. Then, use the 11/16″ socket to push the other cup in far adequate to install the clips. If the cups do not suit, you can use a bearing press to take away them and repeat the procedure. Soon after removing the U-joint, use a grease nipple Make certain the new grease nipple is installed accurately.
Worn or destroyed U-joints are a significant resource of driveshaft failure. If one particular of them have been broken or ruined, the entire driveshaft could dislocate and the automobile would lose electricity. Except if you have a skilled mechanic performing the repairs, you will have to replace the complete driveshaft. The good news is, there are numerous ways to do this your self.
If any of these warning symptoms seem on your car, you ought to take into account changing the damaged or worn U-joint. Frequent signs of ruined U-joints contain rattling or periodic squeaking when moving, rattling when shifting, wobbling when turning, or rusted oil seals. If you notice any of these indicators, consider your automobile to a qualified mechanic for a complete inspection. Neglecting to replace a worn or destroyed u-joint on the driveshaft can end result in expensive and unsafe repairs and can cause significant harm to your vehicle.

